Understanding Self-Excited Generator Circuits in Ultrasonic Generators
Browse Volume:3 Classify:Support
The Role of Ultrasonic Generators in Cleaning Systems
Ultrasonic cleaning systems rely on high-frequency sound waves to generate cavitation bubbles that effectively remove contaminants from surfaces. At the core of these systems lies the ultrasonic generator, responsible for converting electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical vibrations. The efficiency and stability of the ultrasonic cleaning process largely depend on the generator’s circuit design, particularly whether it operates on a self-excited or separately-excited configuration.
Among these designs, self-excited generator circuits stand out due to their simplicity, reliability, and ability to automatically adjust to load variations. This makes them highly suitable for a variety of ultrasonic applications, from industrial cleaning to medical device sterilization.
What is a Self-Excited Generator Circuit?
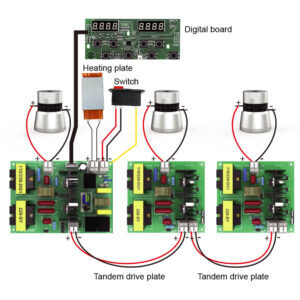
A self-excited generator circuit is a type of electrical circuit that sustains its own oscillations without requiring an external oscillator. Instead, it utilizes positive feedback to maintain and regulate its output frequency. This feature is particularly advantageous in ultrasonic generators, as it allows the circuit to adapt to different transducer loads, optimizing performance dynamically.
In an ultrasonic cleaning system, the self-excited generator works by continuously adjusting to the impedance of the piezoelectric transducer, ensuring efficient energy transfer. This leads to stable cavitation, improved cleaning performance, and reduced power losses.
Key Components of a Self-Excited Generator Circuit
A self-excited generator circuit typically consists of several essential components that work together to achieve consistent ultrasonic wave generation:

- Power Supply Unit: Converts standard AC or DC input into the required voltage level for the circuit.
- Oscillator Circuit: Generates the necessary frequency for driving the transducer.
- Feedback Loop: Regulates the oscillation frequency to match the transducer’s resonance.
- Power Amplifier: Boosts the signal strength before delivering it to the transducer.
- Piezoelectric Transducer: Converts electrical oscillations into mechanical vibrations, which propagate as ultrasonic waves in the cleaning solution.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring that the ultrasonic generator operates efficiently and maintains a stable output frequency.
Advantages of Self-Excited Generator Circuits in Ultrasonic Applications
The self-excited design offers several benefits that make it well-suited for ultrasonic generators:

1. Automatic Frequency Adjustment
One of the most significant advantages of self-excited circuits is their ability to self-tune. The circuit naturally locks onto the resonance frequency of the piezoelectric transducer, ensuring maximum energy transfer and consistent ultrasonic wave generation.
2. Simplified Circuitry and Cost Efficiency
Compared to separately-excited generator circuits, self-excited designs have fewer components, reducing manufacturing costs and simplifying circuit maintenance. The lack of an external oscillator also reduces overall system complexity.
3. Enhanced System Stability
Self-excited generators automatically adjust to fluctuations in load conditions, making them highly stable even in variable operational environments. This is especially useful in industrial ultrasonic cleaning systems where different materials and contaminants can alter the transducer’s operating conditions.
4. Energy Efficiency
Since the circuit continuously optimizes frequency and power delivery, it reduces unnecessary energy consumption, leading to lower operating costs and extended equipment lifespan.
Challenges and Considerations in Self-Excited Generator Design
While self-excited generator circuits offer multiple benefits, they also present some challenges that need to be addressed during design and implementation:
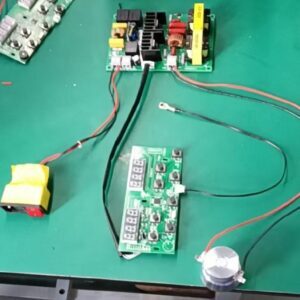
1. Sensitivity to Load Variations
Although self-excited circuits can adapt to load changes, extreme variations in transducer impedance can cause instability. Proper component selection and circuit tuning are essential to minimize this effect.
2. Circuit Drift and Frequency Stability
Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations can affect the components, leading to frequency drift. Implementing temperature compensation techniques and high-quality components can help mitigate this issue.
3. Limited Frequency Range
Self-excited circuits typically work best within a specific frequency range. Applications requiring precise frequency control, such as medical ultrasound devices, may benefit more from separately-excited generator designs.
Applications of Self-Excited Ultrasonic Generators
Self-excited generator circuits are widely used in various ultrasonic applications due to their adaptability and efficiency. Some of the most common applications include:

- Industrial Cleaning: Used in cleaning machinery parts, metal components, and automotive parts where reliable cavitation is necessary.
- Medical Equipment Sterilization: Helps in cleaning surgical instruments and delicate medical devices without causing damage.
- Jewelry and Precision Instruments: Effectively removes dirt and residues from intricate designs and delicate materials.
- Electronics and Semiconductor Industry: Cleans circuit boards and electronic components without using harsh chemicals or excessive manual labor.
Future Developments in Self-Excited Ultrasonic Generator Circuits
With advancements in power electronics and digital control technology, self-excited ultrasonic generator circuits are expected to become even more efficient and adaptable. Some emerging trends include:

- Integration with Digital Signal Processing (DSP): Enhancing frequency control and real-time feedback adjustments.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Optimization: Using machine learning algorithms to fine-tune performance and predict maintenance needs.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Developing energy-efficient circuits that reduce power consumption and extend equipment lifespan.
As industries continue to demand more precise and energy-efficient ultrasonic systems, self-excited generator circuits will play a crucial role in meeting these requirements. By improving their design and addressing existing limitations, manufacturers can further enhance their performance, making them a preferred choice for ultrasonic applications worldwide.
References
- Mason, T. J., & Lorimer, J. P. (2002). “Applied Sonochemistry: The Uses of Power Ultrasound in Chemistry and Processing.” Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/3527601543
- Ensminger, D., & Bond, L. J. (2011). “Ultrasonics: Fundamentals, Technologies, and Applications.” CRC Press. doi:10.1201/b10752
- Culjat, M. O., Goldenberg, D., Tewari, P., & Singh, R. S. (2010). “A Review of Tissue Substitutes for Ultrasound Imaging.” Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 36(6), 861-873. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.02.012
 GranboUltrasonic
GranboUltrasonic